An Example Azure DevOps Release Pipeline for PowerShell modules
Introduction
In the previous post I went over an example Azure DevOps Build Pipeline for PowerShell modules. This post will continue from where we left off and discuss the Azure DevOps Release Pipeline for PowerShell modules.
I’ll go over the different stages, and explain how the PowerShell modules are released to multiple internal Artifact feeds.
Azure DevOps Release Pipeline
First, let’s look at the example Azure DevOps Release Pipeline for my PowerShell module. My Azure DevOps project visibility is public for all to see, so you shouldn’t be prompted for a login.
The purpose of this Release Pipeline is to take Artifacts from the Build Pipeline, and release them to a stage. Here’s an example release showing deployments to all three stages (Dev, Test, and Prod).
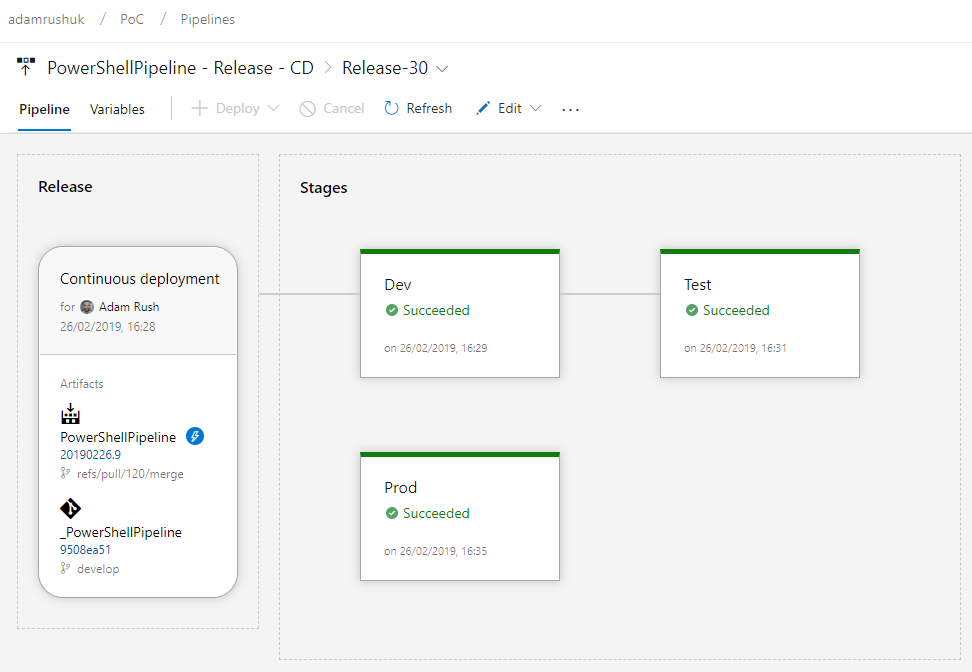
Artifacts
In the Release section above you can see the PowerShellPipeline Artifacts appear under the Continuous deployment heading. This shows a Release is triggered every time a Build Pipeline creates those Artifacts.
Dev Stage
We now move on to the stages. Note there is a line between Artifacts and the Dev stage, due to a Pre-deployment condition trigger set to After release:
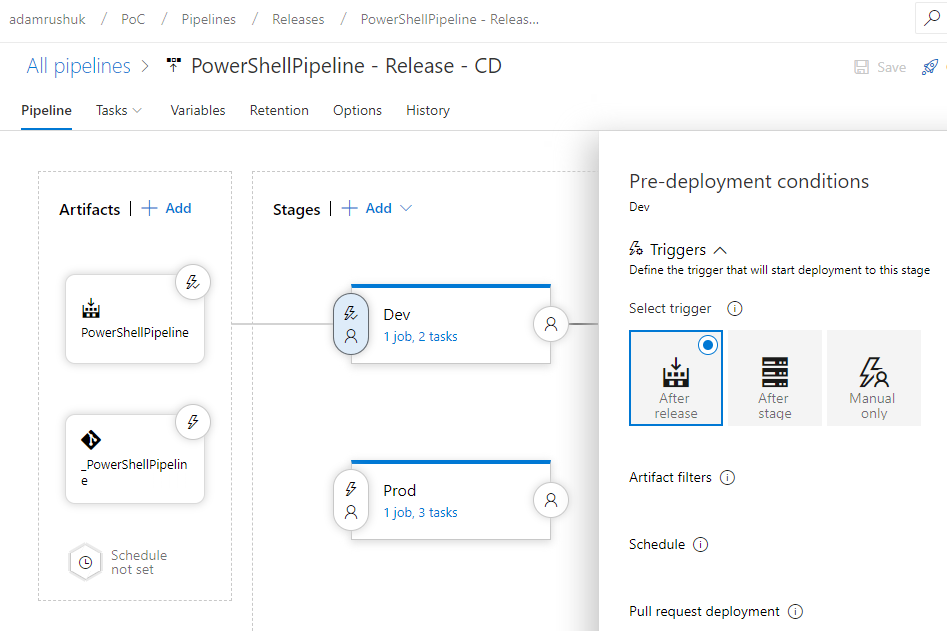
This setting ensures the Dev stage is triggered automatically without user intervention.
Test Stage
The Test stage trigger is configured to start after the previous Dev stage, using an After stage trigger:
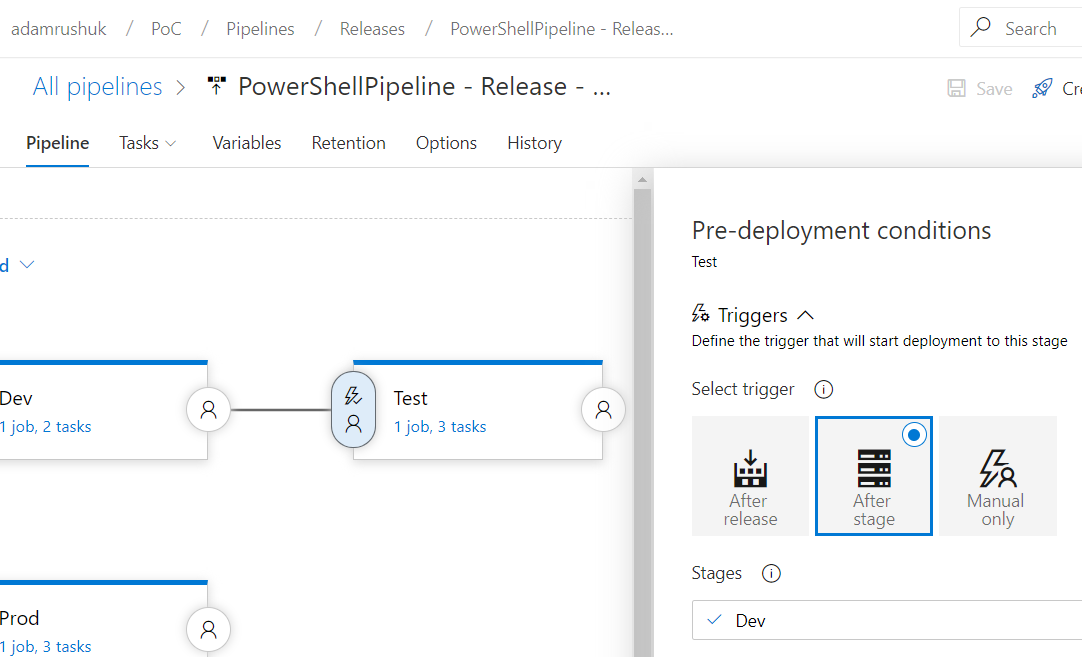
Prod Stage
Lastly, the Prod stage has a Manual only trigger:
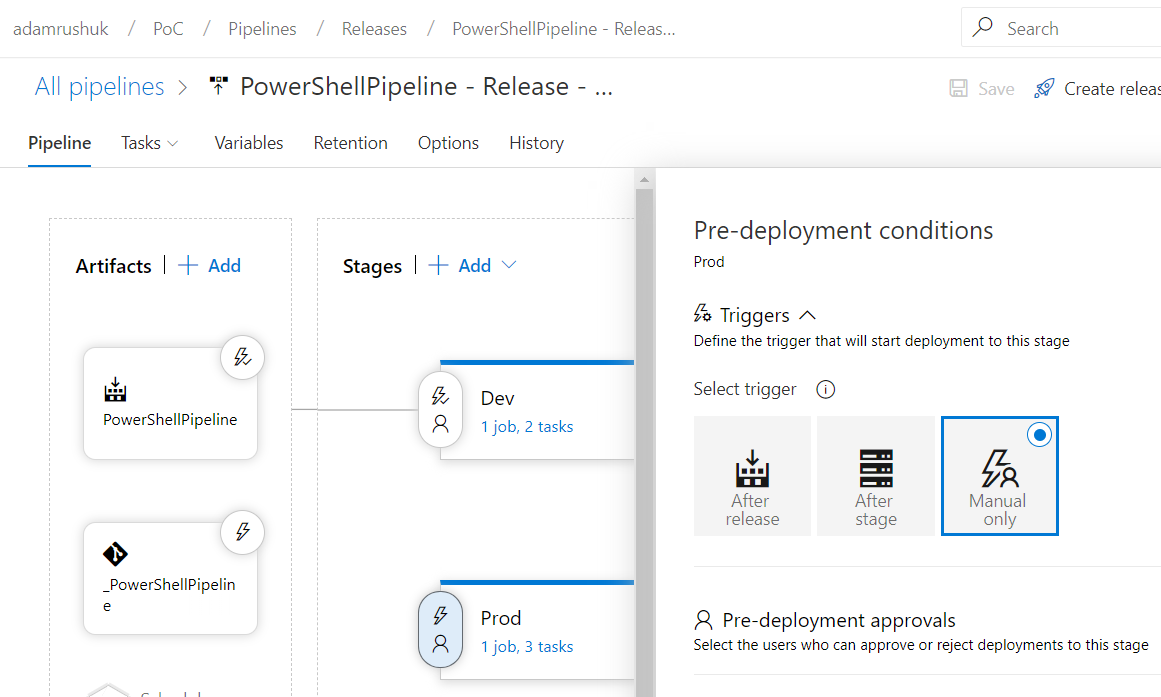
This gives us the option to manually validate the Dev and Test environments are working as expected before we release to Prod.
Stage Tasks
All stages use roughly the same tasks, but let’s take a closer look into Prod:
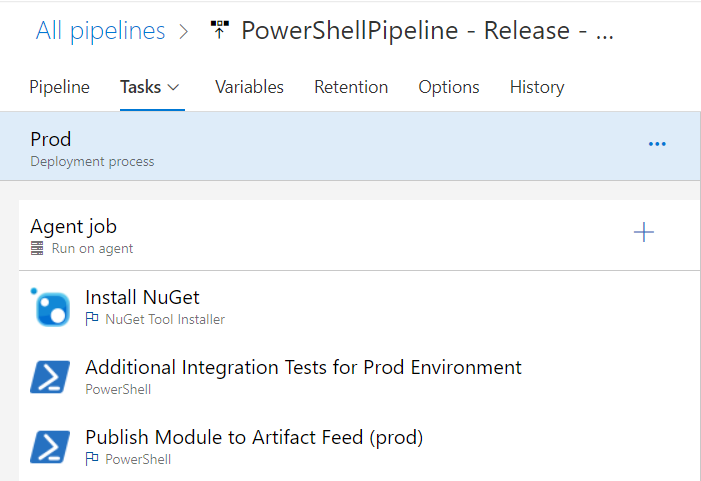
Install NuGet
The Install NuGet task is self-explanatory, and simply installs the specified NuGet binary version. NuGet is required to publish PowerShell modules to our internal Artifact feed.
Additional Integration Tests for Prod Environment
This task is a placeholder for actual test code, just to highlight you could run integration tests at this point if required. This might include provisioning infrastructure, loading data, then running tests and publishing the test results.
Publish Module to Artifact Feed (prod)
The final task is responsible for running a PowerShell script called Publish-AzDOArtifactFeed.ps1, which takes
two parameters: AzDOArtifactFeedName and AzDOPat:
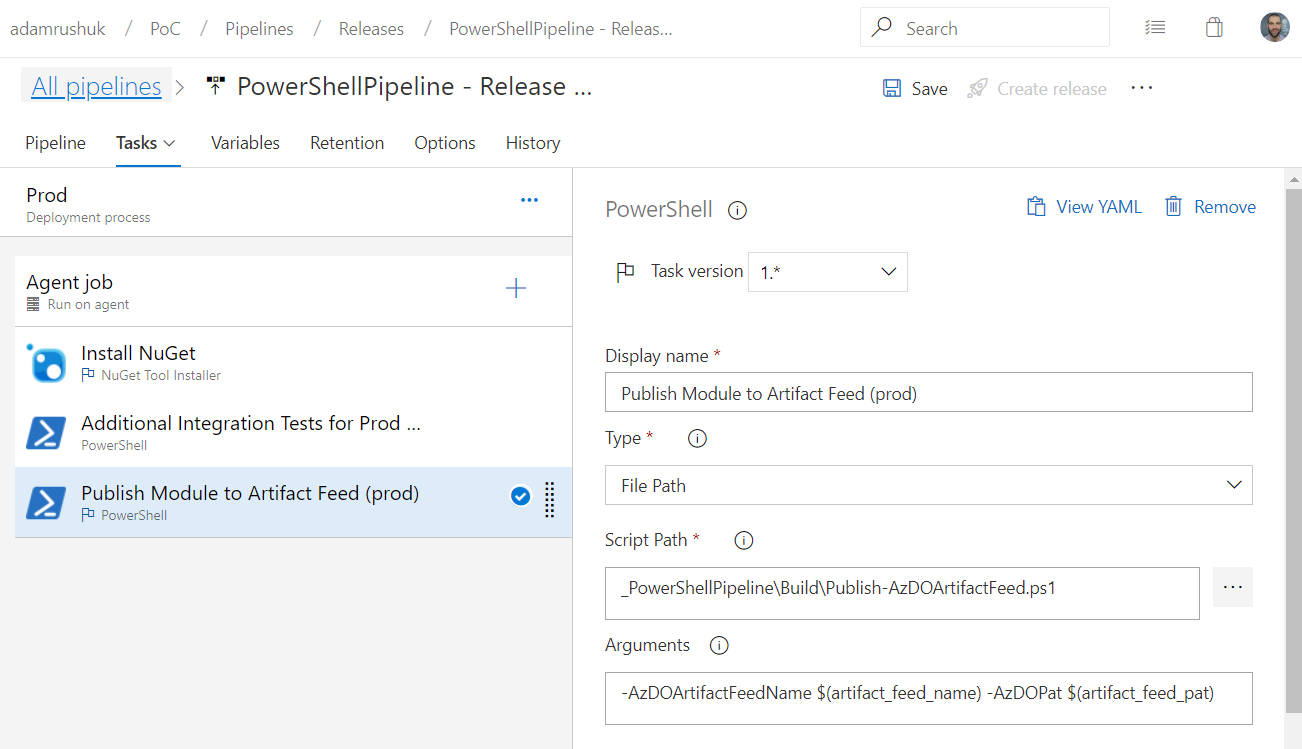
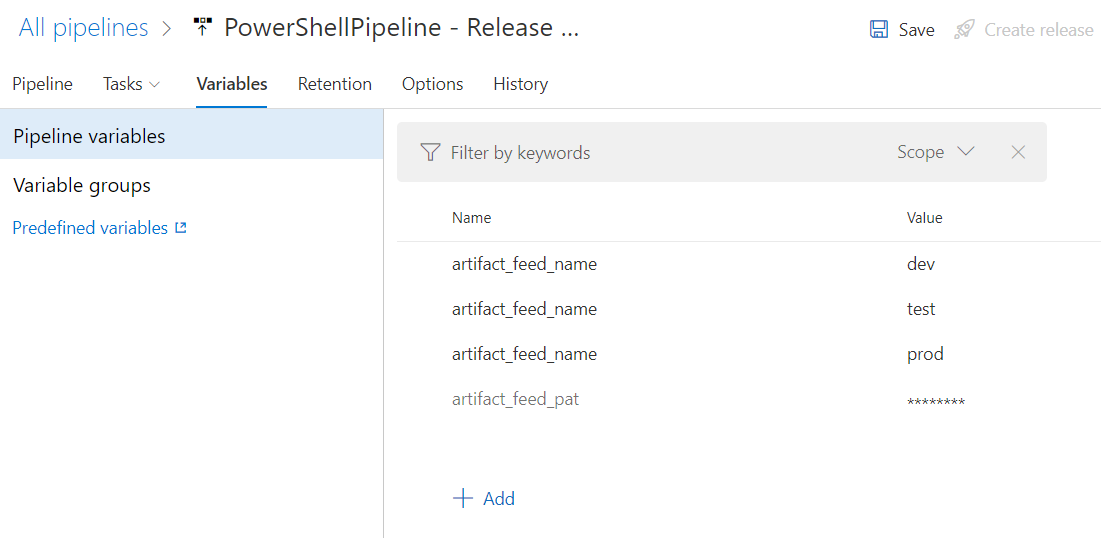
The Arguments field shown above references Pipeline Variables $(artifact_feed_name) and $(artifact_feed_pat),
shown below:
Publish-AzDOArtifactFeed.ps1
The code below has comments throughout, but the main steps are:
- Register a NuGet Package Source.
- Register a PowerShell Repository.
- Publish a PowerShell module.
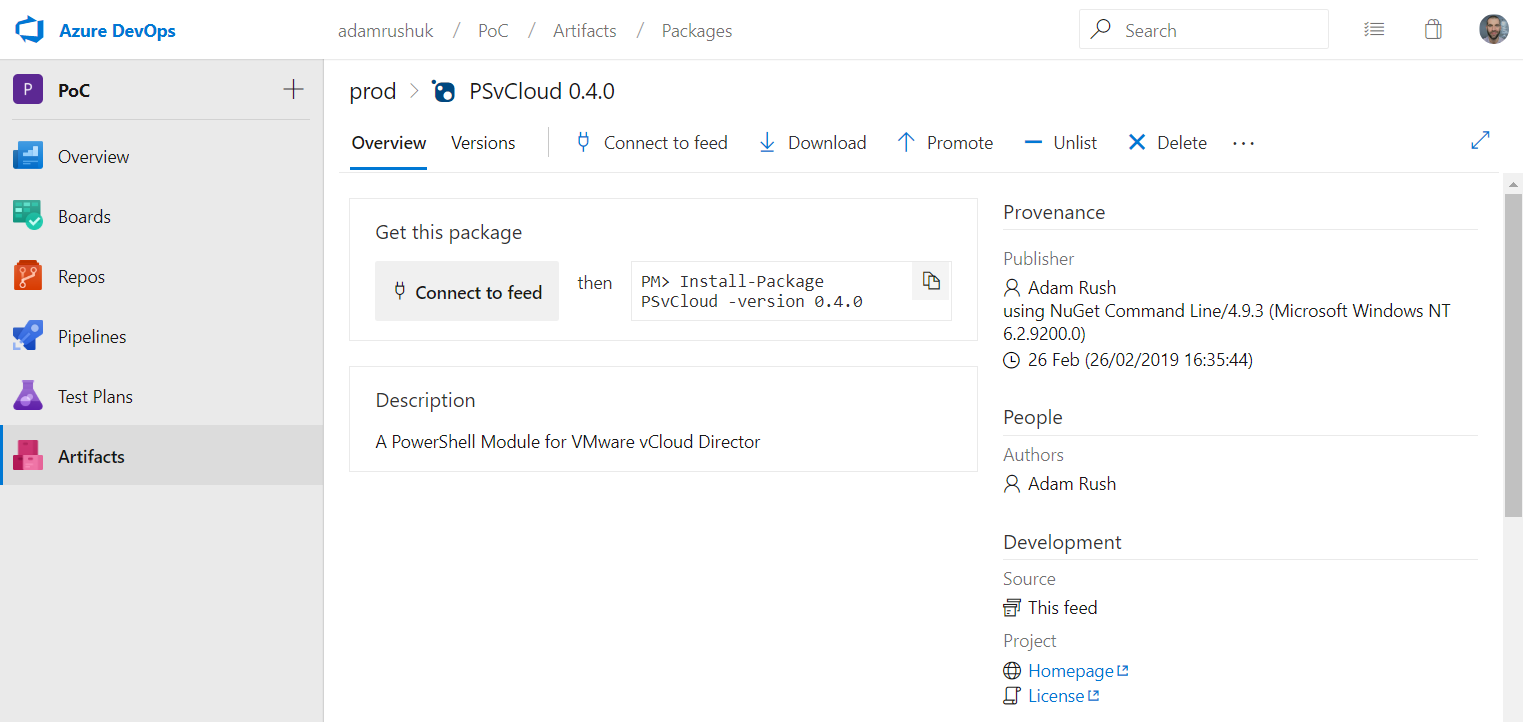
Azure Artifacts Feed
Once the PowerShell module has been published by the Publish-AzDOArtifactFeed.ps1 script, the new NuGet package
is available within the specified Azure Artifacts feed (eg. prod):



Leave a comment