An Example Azure DevOps Build Pipeline for PowerShell modules
Introduction
A few months ago did a demo at the Bristol WinOps Meetup showing an example Azure DevOps Build Pipeline for PowerShell modules. I told everyone I’d get a blog post up “soon” with more information, so here it is; better late than never!
I’ll go over the goals for the example PowerShell Module, then break down the Build Pipeline tasks for Azure DevOps.
Goals for the Example PowerShell Module (PSvCloud)
PSvCloud was a very old PowerShell module I started working on several years ago whilst I was using VMware vCloud every day. I changed jobs shortly after starting it, so didn’t add much. However, it was good enough as an example module for the Azure DevOps Build Pipeline.
I applied the latest methods and best practices learned at the time to PSvCloud, with a focus on the process around
The Release Pipeline Model (Source > Build > Test > Release).
Source
Git was used with the practical common flow branching model.
Build
psake was used to develop build scripts that can be used both locally using Task Runners in Visual Studio Code, and by a CI/CD system like Azure DevOps.
This covers:
- Compiling separate function files into a single .psm1 module.
- Automatically updating documentation in Markdown, ready for a 3rd-party like ReadTheDocs.
Test
Testing the compiled code for known issues and ensuring it aligned to defined standards.
This covers:
- Code analysis using PSScriptAnalyzer.
- Code testing (unit, and common) using Pester.
Release
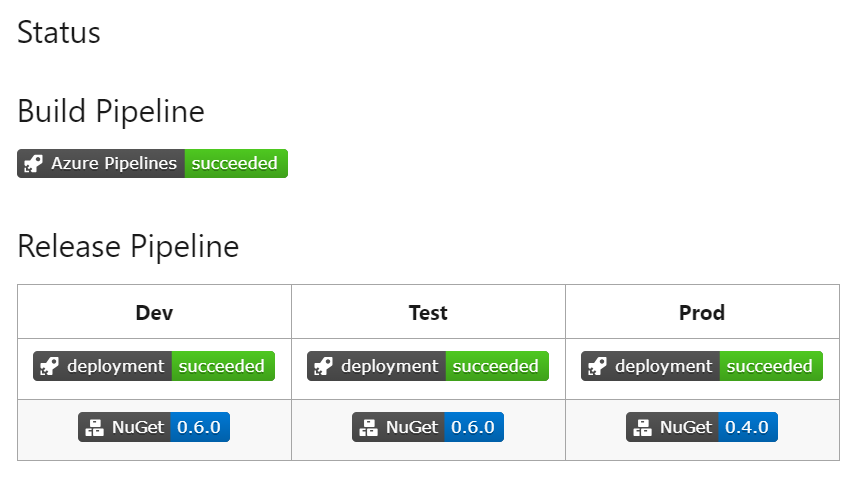
Publishing the module build artifact to multiple Azure DevOps Artifacts (NuGet) feeds; one per environment. Each environment shows the current version available using Status Badges:
Build Pipeline Tasks for Azure DevOps
For the build pipeline definition I opted for the YAML method, opposed to GUI method. Using a YAML file allowed me to save the file within my repo alongside all other files under source control.
I’ll go over each build step below, but you can also view the complete file, azure-pipelines.yml.
build.ps1
You’ll notice below that every task name is passed to a script called build.ps1. This script is responsible for bootstrapping the environment - ensuring all dependencies are installed - initialising environment variables, and finally invoking the specified build task(s).
Init
- powershell: |
.\Build\build.ps1 -ResolveDependency -TaskList 'Init'
displayName: "Install Dependencies"
The Init task includes the -ResolveDependency switch which triggers the use of PSDepend.
PSDepend uses the
psvcloud.depend.psd1
config file to install the required PowerShell modules.
CombineFunctionsAndStage
- powershell: |
.\Build\build.ps1 -TaskList 'CombineFunctionsAndStage'
displayName: "Combine PowerShell functions into single module file"
The CombineFunctionsAndStage task combines all public and private PowerShell functions into single module file,
then stages other required folders and files like /Documentation, /Examples, and README.md.
Analyze
- powershell: |
.\Build\build.ps1 -TaskList 'Analyze'
displayName: "Analyze"
The Analyze task runs PSScriptAnalyzer against the code to ensure quality and best practices are used.
Test
- powershell: |
.\Build\build.ps1 -TaskList 'Test'
displayName: "Test"
The Test task runs the Pester tests located in /Tests.
UpdateDocumentation
- powershell: |
.\Build\build.ps1 -TaskList 'UpdateDocumentation'
displayName: "Update Documentation"
The UpdateDocumentation task uses PlatyPS to create new documentation markdown files from the comment-based help within each PowerShell function.
CreateBuildArtifact
- powershell: |
.\Build\build.ps1 -TaskList 'CreateBuildArtifact'
displayName: "Create Build Artifact"
The CreateBuildArtifact task creates a versioned zip file of all staged files.
PublishTestResults
- task: PublishTestResults@2
displayName: "Publish Pester Tests"
inputs:
testRunner: "NUnit"
searchFolder: "Artifacts"
testRunTitle: "PesterTests"
condition: always()
The PublishTestResults task publishes any Pester results files (NUnitXml) it finds in the Artifacts folder.
PublishBuildArtifacts 1
- task: PublishBuildArtifacts@1
displayName: "Publish Artifact: PowerShell Module Zipped for offline use"
inputs:
PathtoPublish: Artifacts
ArtifactName: Artifacts
condition: always()
The first PublishBuildArtifacts task publishes the versioned PowerShell zip file, which is ready to download for offline use.
PublishBuildArtifacts 2
- task: PublishBuildArtifacts@1
displayName: "Publish Artifact: PowerShell Module"
inputs:
PathtoPublish: Staging
ArtifactName: PSModule
condition: always()
The second PublishBuildArtifacts task publishes the whole /Staging folder as is (not zipped), to be used in the
Release Pipeline.
What’s Next?
My next post will cover an example Azure DevOps Release Pipeline for PowerShell modules



Leave a comment